GreenTech-Renovation
Energetische Sanierung von gläsernen Gebäuden von architektonischem Wert
Forschungsprojekt, Demonstrationsprojekt ENERGIE DER ZUKUNFT, FFG Stadt der Zukunft 8. Ausschreibung, 4. Nachhaltige Sanierung, 4.3 Demonstration nachhaltiger Gebäude- und Quartiersanierung
Status: abgeschlossen
Kreislaufwirtschaft, Bauen im Bestand, Revitalisierung, Sanierung, Renovierung, Energieeffizienz, Erneuerbare Energiequellen
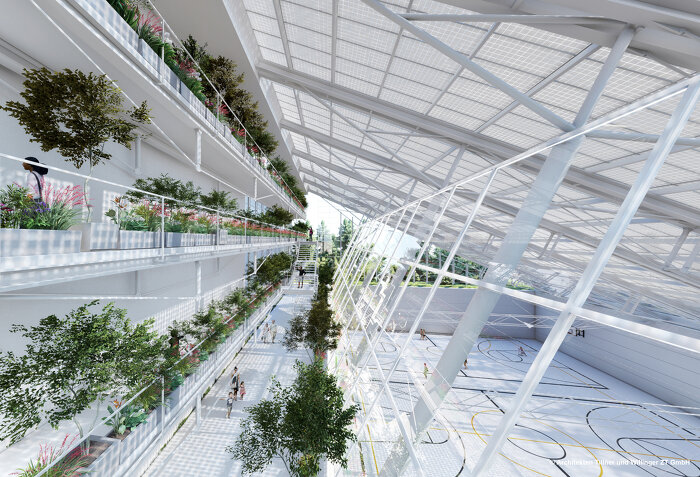
Der Schwerpunkt des Projekts GreenTech-Renovation ist, innovative Lösungen zur energetischen Sanierung von architektonisch wertvollen Bauten mit hohen Glasanteil zu finden. Dafür soll ein zukunftsweisendes bauphysikalisches Konzept entwickelt werden das den Einsatz alternativer Energieformen beinhaltet. Ein intelligentes Nutzungskonzept verstaerkt mit ökologischem und sozialem Engagement die energetischen Sanierungskonzepte und deren Nachhaltigkeit garantieren. Die 10 R der Kreislaufwirtschaft dienen dabei als Leitlinie .
Ausgangssituation/Motivation
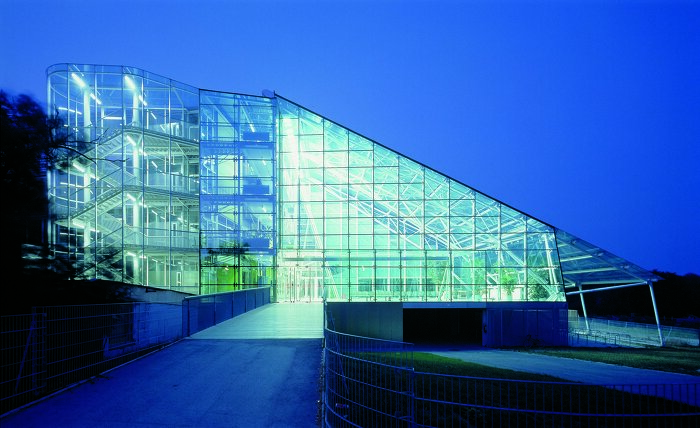
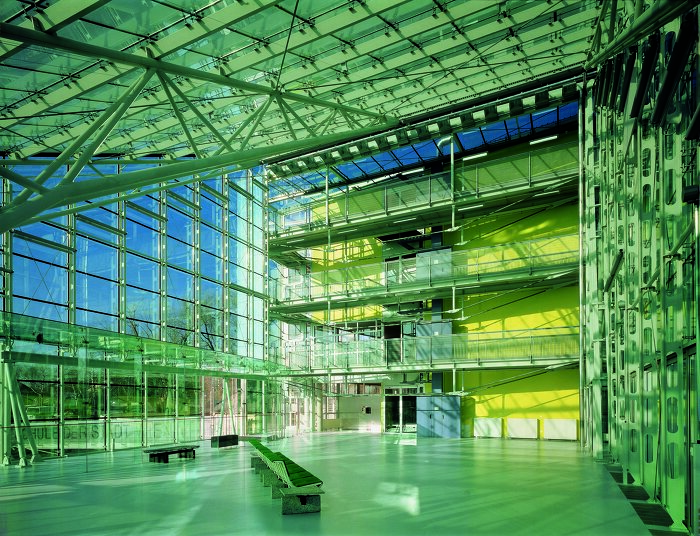
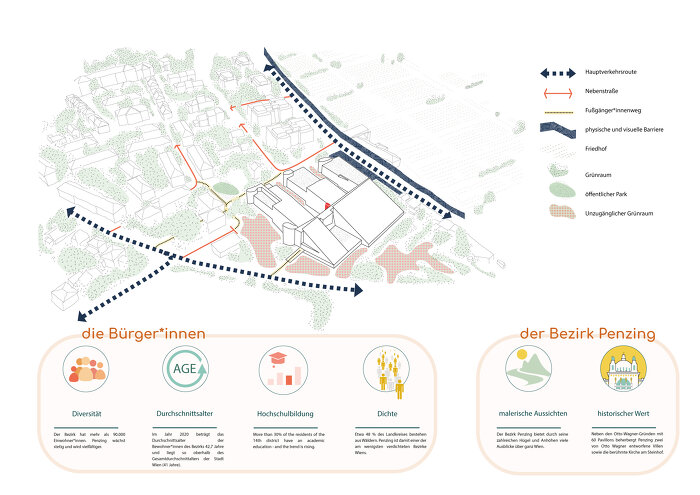
Die Klimapolitik sieht einen dringenden Bedarf an energetischer Sanierung von Bestandsbauten. Eine besondere Herausforderung stellen Bauten mit denkmalpflegerischem, bzw. architektonischem Wert dar. Sie sind Teil unseres kulturellen Erbes und verdienen deshalb unabhängig von ihrem Schutzstatus besondere Aufmerksamkeit bei der Sanierung. Als Demonstrationsprojekt für diese Forschungsarbeit soll die Schule am Kinkplatz von Helmut Richter dienen, da bei diesem Gebäude exemplarisch sehr viele Themen zur sinnvollen energetischen Sanierung bearbeitet werden können.
Inhalte und Zielsetzungen
Schwerpunkt der Forschung ist innovative Lösungen zur energetischen, ökologischen und sozialen Revitalisierung von architektonisch wertvollen Bauten mit hohen Glasanteil zu finden.
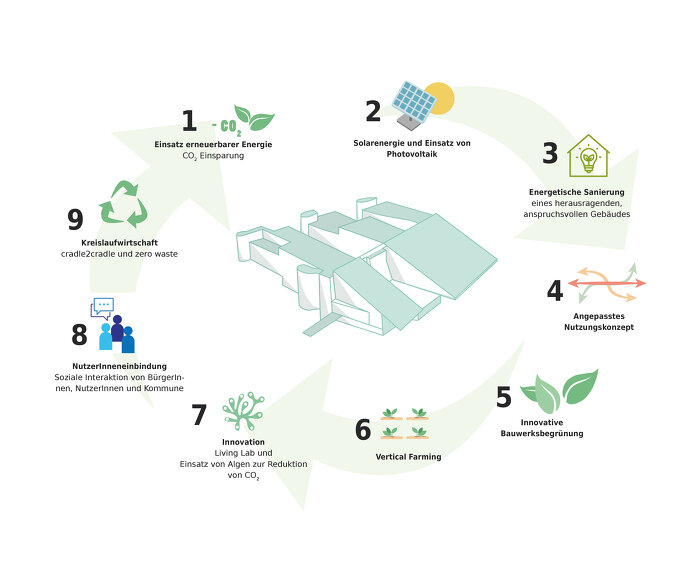
Es sollen Querverbindungen zu aktuell laufenden Initiativen auf europäischer Ebene hergestellt werden, da das gegenständliche Sondierungsprojekt diese auf mehreren Ebenen trefflich erfüllt. Die Themen: CO2 Einsparung, Kreislaufwirtschaft, Sanierung eines herausragenden, anspruchsvollen Gebäudes, angepasstes Nutzungskonzept, Innovation, Einsatz erneuerbarer Energie, Bauwerksbegrünung, Nutzereinbindung finden sich alle in dem Projekt “Green-Tech Renovation” wieder.
Das Ziel ist die Entwicklung von verschiedenen Lösungskonzepten die die gestellte Aufgabe unter den Hauptbedingungen erfüllen und deren Bewertung. Die Konzepte sollen ein breites Spektrum abdecken und innovative Ansätze verfolgen.
Methodische Vorgehensweise
Internationale Referenzprojekte sollen analysiert werden, um verwertbar strukturierte und vergleichbare Daten zu liefern. Das Revitalisierungskonzept soll darauf aufbauend holistisch entwickelt, aber die Maßnahmen für die unterschiedlichen Teilbereiche des Objekts in einzelne Komponenten zerlegt werden. Durch die Aufgliederung im Sinne einer „Mustersprache“ in Bereiche, Bauteile und Komponenten werden auch Erkenntnisse aus Teilbereichen wertvolle verwertbare Daten für vergleichbare Projekte liefern.
Die 10 R der Kreislaufwirtschaft (Refuse, Rethink, Reduce, Reuse, Repair, Refurbish, Remanufacture, Repurpose, Recycle, Recover) und ein noch zu erstellender Leitfaden zur „Kreislaufwirtschaft im Hochbau“ für den Bestand werden zur Strukturierung der Vorgehensweise herangezogen.
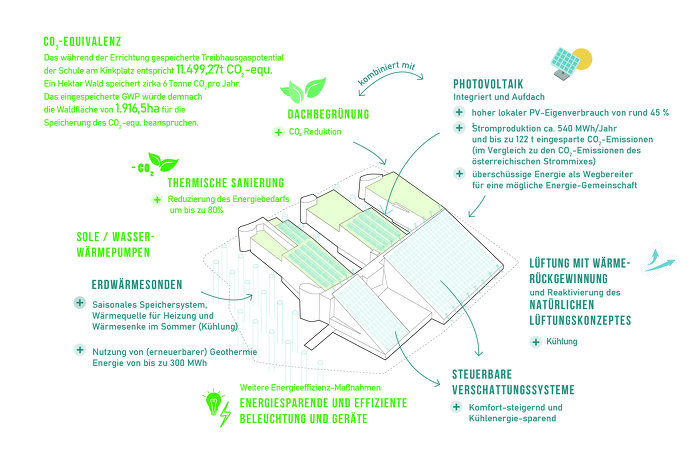
Die energetische Sanierung soll unter dem Einsatz erneuerbarer Energien z.B. Photovoltaik und Umgebungswärme in Kombination mit erforderlicher Solarthermie zur Regenerierung der Erdsonden im verfügbaren Rahmen erfolgen. Dafür wird ein zukunftsweisendes bauphysikalisches Konzept mit Speichermöglichkeiten und dem Ziel entwickelt, Energie optimal lokal zu nutzen und CO2 zu vermeiden sowie den Energieverbrauch und somit die Erhaltungskosten stark zu senken.
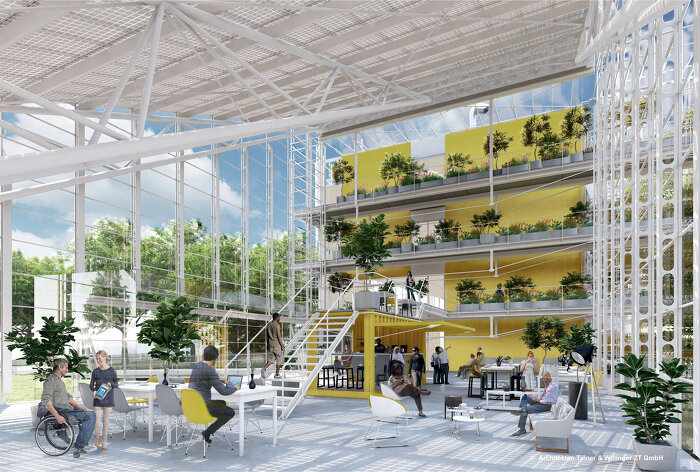
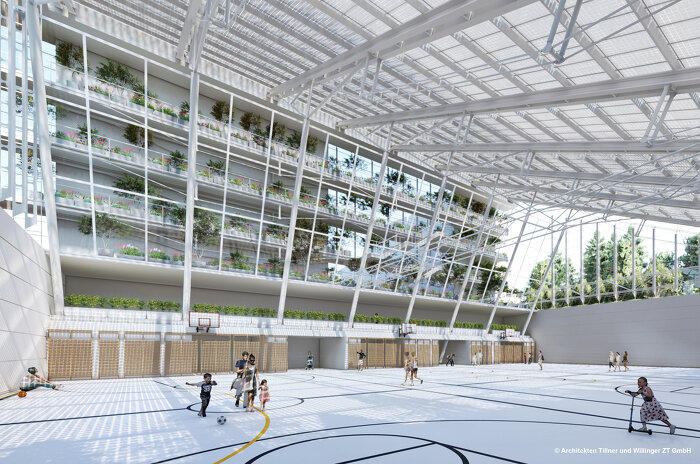
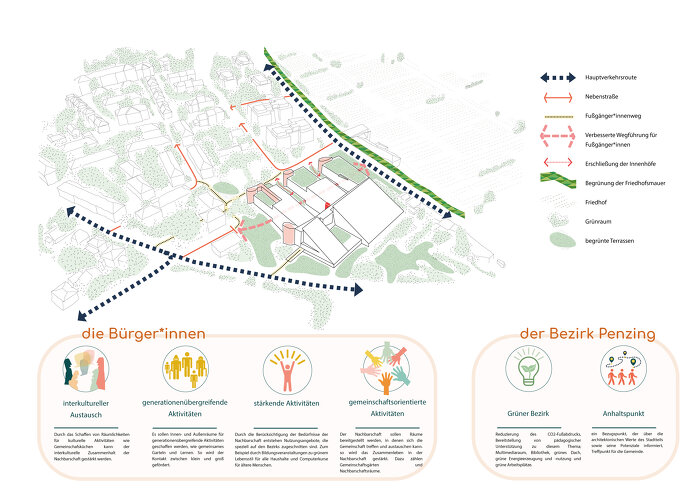
Die Gebäude adäquate Nutzung stellt eine zentrale Frage bei der energetischen Sanierung dar, da sie zu zielgerichteten, effizienten und im Sinne von „Reduce“ minimierten Baumaßnahmen führt. In der Analyse- und Planungsphase werden ff. wesentliche Fragen gestellt: Was sind die architektonischen Qualitäten des Gebäudes bzw. der Gebäudezonen? Und welche Nutzung entspricht diesen Qualitäten am besten und ist mit minimalinvasiven Eingriffen dafür geeignet?
Im Forschungsprojekt sollen dem Gebäude entsprechende adäquate Nutzungsmöglichkeiten untersucht werden. Die vorgeschlagene Vorgangsweise, aufbauend auf den räumlichen Qualitäten und den darin technisch machbaren, sinnvollen Maßnahmen, passende Nutzungen zu finden, stellt eine Umkehrung der üblichen Praxis dar. Effiziente, minimierte bauliche Eingriffe eröffnen großes Einsparpotential im Materialeinsatz, CO2 Ausstoß und in den Kosten.
Begrünung als Synergiemaßnahme spielt bei dem Projekt eine verbindende Rolle. Wir adressieren die Ziele: Stärkung der internationalen Wettbewerbsfähigkeit österreichischer Unternehmen und Forschungsinstitute, intelligenter Energielösungen und Beitrag zur Entwicklung resilienter Städte und Stadtteile
Erwartete Ergebnisse
Die Erkenntnisse des Forschungsprojektes sollen in einer Handlungsempfehlung für ein Sanierungskonzept der ehemaligen Schule am Kinkplatz zusammengefasst werden. Zudem werden die in Varianten entwickelten Lösungen für zukünftige Projekte eine wertvolle Grundlage liefern. Die Strategien werden so aufbereitet und strukturiert, dass sie bei weiteren Revitalisierungsprojekten von schützenswerten Bauten mit hohem Glasanteil angewandt werden können. Eine Handlungsanleitung wird aufbauend auf dem Leitfaden zur Kreislaufwirtschaft im Hochbau für Folgeprojekte zur Verfügung stehen.
- Adresse:
- Kinkplatz 21, 1140 Wien, Österreich
- Architektur:
- Architekten Tillner & Willinger, Wien
- Mitarbeit Architektur:
- DI Sophie Stockhammer, DI Mahshid Rezaei
- Tragwerksplanung:
- Technische Universität Wien
- Bauphysik:
- IBO Österreichisches Institut für Bauen und Ökologie
- Energie:
- FH Technikum Wien - Fachhochschule Wien
- Begrünung:
- GrünStattGrau
- KonsulentInnen:
- IBO – Österreichisches Institut für Bauen und Ökologie GmbH
Technische Universität Wien, Forschungsbereich für Tragwerksplanung und Ingenieurholzbau
Fachhochschule Technikum Wien, Kompetenzfeld für Erneuerbare Energiesysteme
GRÜNSTATTGRAU Forschungs- und Innovations GmbH
vertical farm institute
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Laboratorium für Techniken und Denkmalpflege moderner Architektur
Hubmann Vass Architekten - Planung:
- 2021 - 2022